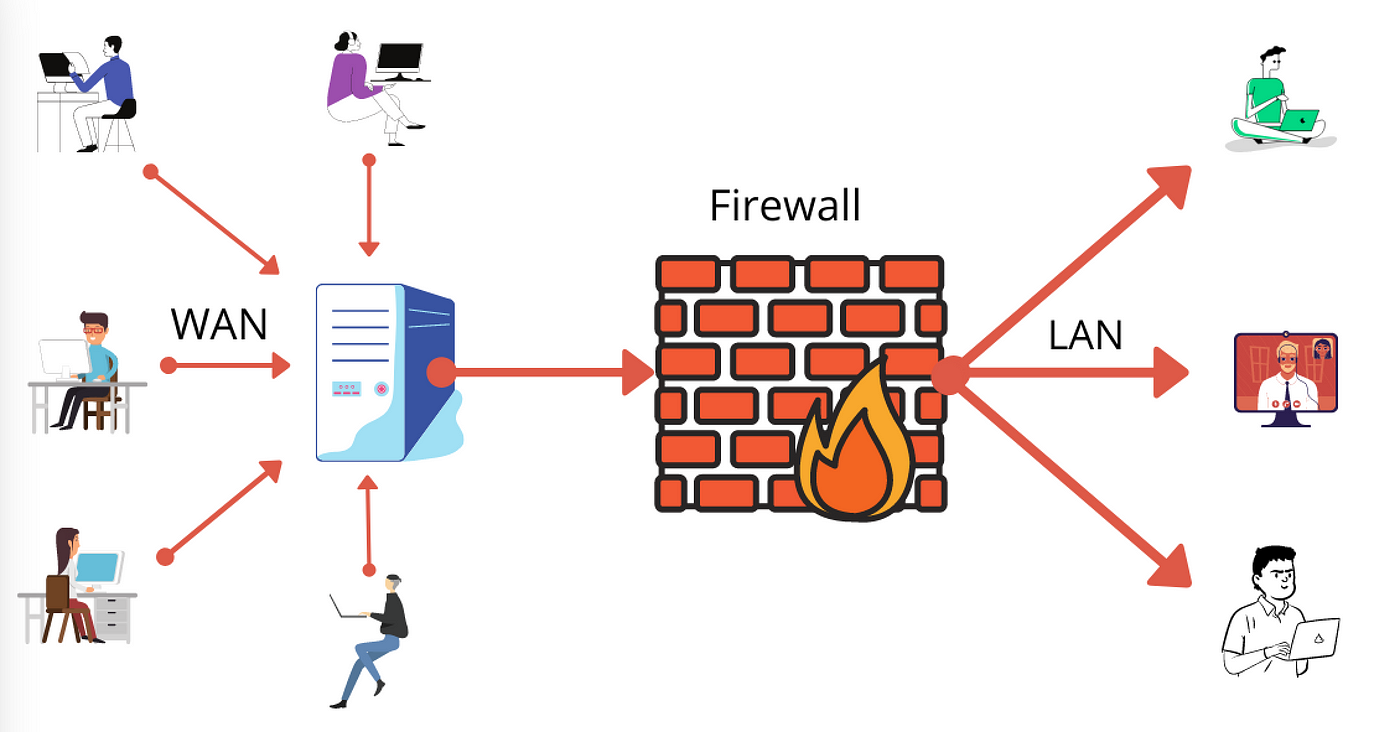
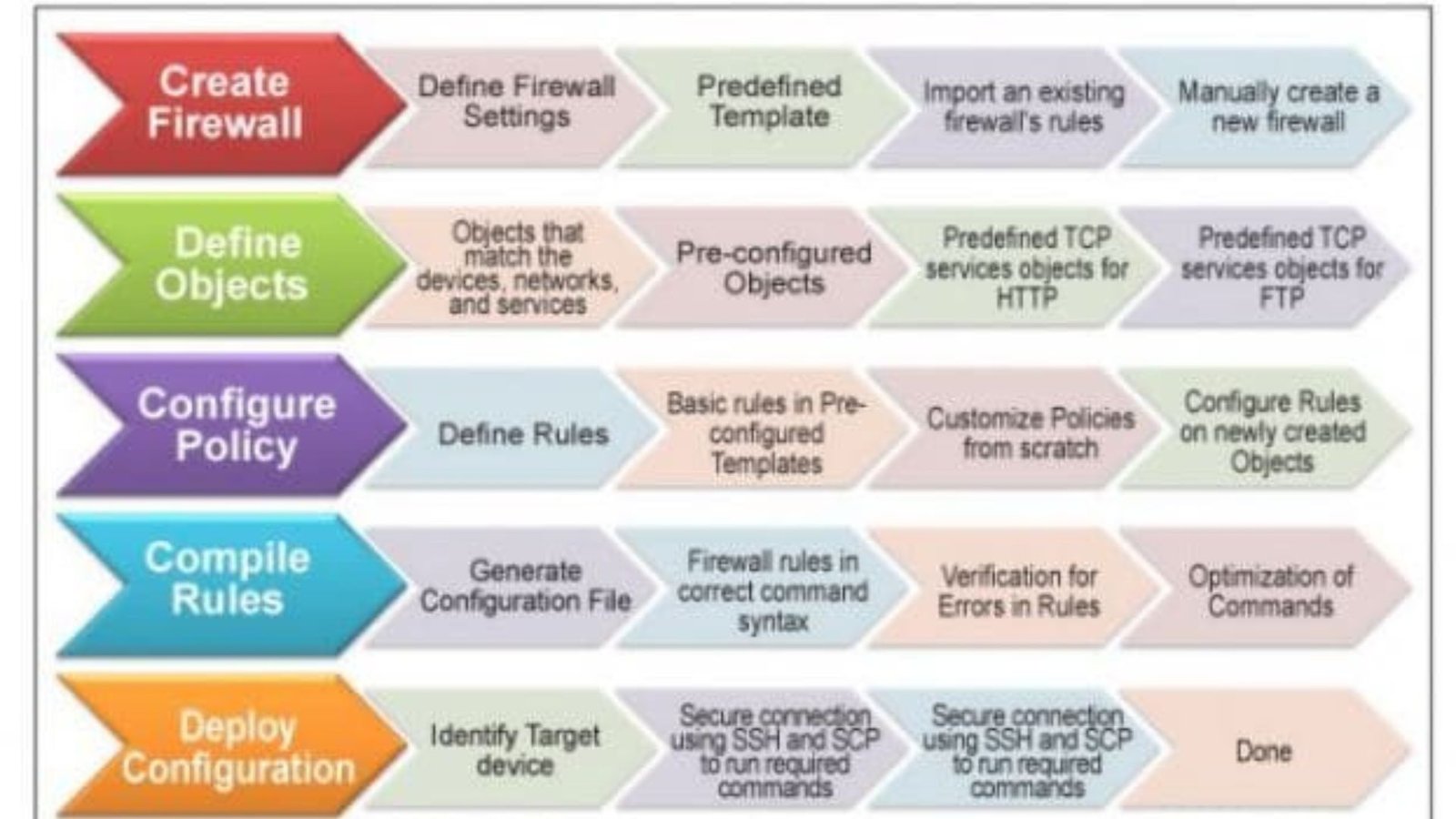
In today’s digital age, cyber threats and attacks are increasingly sophisticated, making robust network security essential for any organization. Firewalls are a crucial line of defense, designed to prevent unauthorized access and protect your network from various cyber threats. This article explores how firewalls work to shield your systems from attacks and ensure data security.
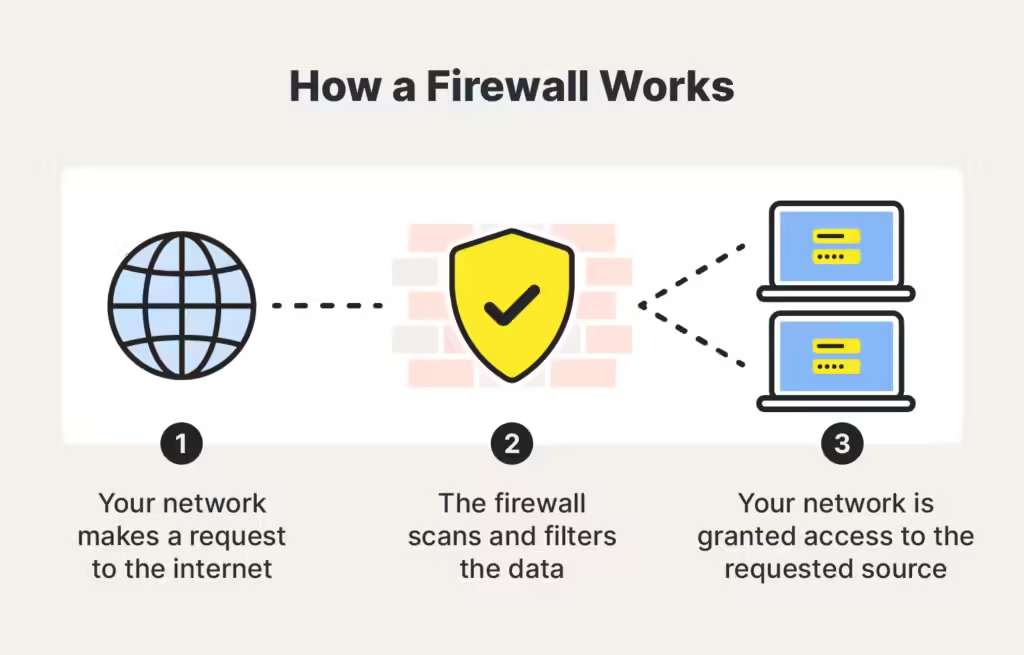
1. Filtering Incoming and Outgoing Traffic
At the core of a firewall’s functionality is its ability to filter traffic based on predefined security rules. A firewall monitors both incoming and outgoing data packets, ensuring that only legitimate traffic is allowed through. By blocking malicious traffic, firewalls prevent hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities in your network.
2. Blocking Unauthorized Access
One of the primary roles of a firewall is to block unauthorized access to your network. By establishing a barrier between your internal network and the external internet, firewalls prevent attackers from infiltrating your system. This is particularly important in protecting sensitive data and critical infrastructure from cybercriminals.
3. Protecting Against Malware and Viruses
Firewalls are effective in defending against malware and viruses by identifying and blocking malicious traffic before it reaches your network. Many firewalls come with integrated antivirus and anti-malware capabilities, which scan data packets for known threats. By stopping these threats at the network’s edge, firewalls prevent them from infecting your systems.
4. Preventing Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks aim to overwhelm a network with excessive traffic, causing it to slow down or crash. Firewalls help prevent DoS attacks by identifying and filtering out suspicious traffic patterns. They can limit the rate of traffic to your network, ensuring that legitimate users maintain access even during an attack.
5. Controlling Access with Network Segmentation
Firewalls allow for network segmentation, which involves dividing your network into smaller, isolated sections. By controlling access between these segments, firewalls limit the ability of attackers to move laterally within your network if they manage to breach one area. This containment strategy minimizes the damage caused by a successful attack.
6. Monitoring and Logging Network Activity
Firewalls provide detailed logs of network activity, which are invaluable for monitoring potential security threats. These logs include information on attempted connections, blocked traffic, and unusual activities. By analyzing this data, network administrators can identify patterns that may indicate an ongoing or impending attack, allowing for a swift response.
7. Establishing Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Many firewalls support Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), which encrypt data transmitted between remote users and the main network. VPNs ensure that sensitive information remains secure even when accessed from outside the organization. By establishing secure connections, firewalls prevent attackers from intercepting or tampering with data during transmission.
8. Implementing Stateful Inspection
Stateful inspection, also known as dynamic packet filtering, is a method used by firewalls to monitor the state of active connections and determine which network packets should be allowed through. Unlike simple packet filtering, which only checks the header of a packet, stateful inspection examines the entire packet and its context within a traffic session. This allows the firewall to make more informed decisions and better protect against complex attacks.
9. Enhancing Security with Application Layer Filtering
Modern firewalls often include application layer filtering, which provides deeper inspection of traffic based on the specific applications or services being used. This type of filtering enables the firewall to block or allow traffic based on the behavior of the application, rather than just its port or protocol. By understanding the context of the traffic, application layer filtering offers enhanced protection against sophisticated threats that target specific applications.
10. Defending Against Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks trick users into providing sensitive information by posing as legitimate entities. Firewalls can help prevent phishing by blocking access to known malicious websites and filtering out phishing emails. Some advanced firewalls include URL filtering and email security features, which further protect users from falling victim to phishing schemes.
Conclusion
Firewalls are a fundamental component of network security, protecting against a wide range of cyber threats and attacks. By filtering traffic, blocking unauthorized access, and providing advanced security features like stateful inspection and application layer filtering, firewalls play a crucial role in safeguarding your network. Implementing a well-configured firewall is essential for any organization looking to defend against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.