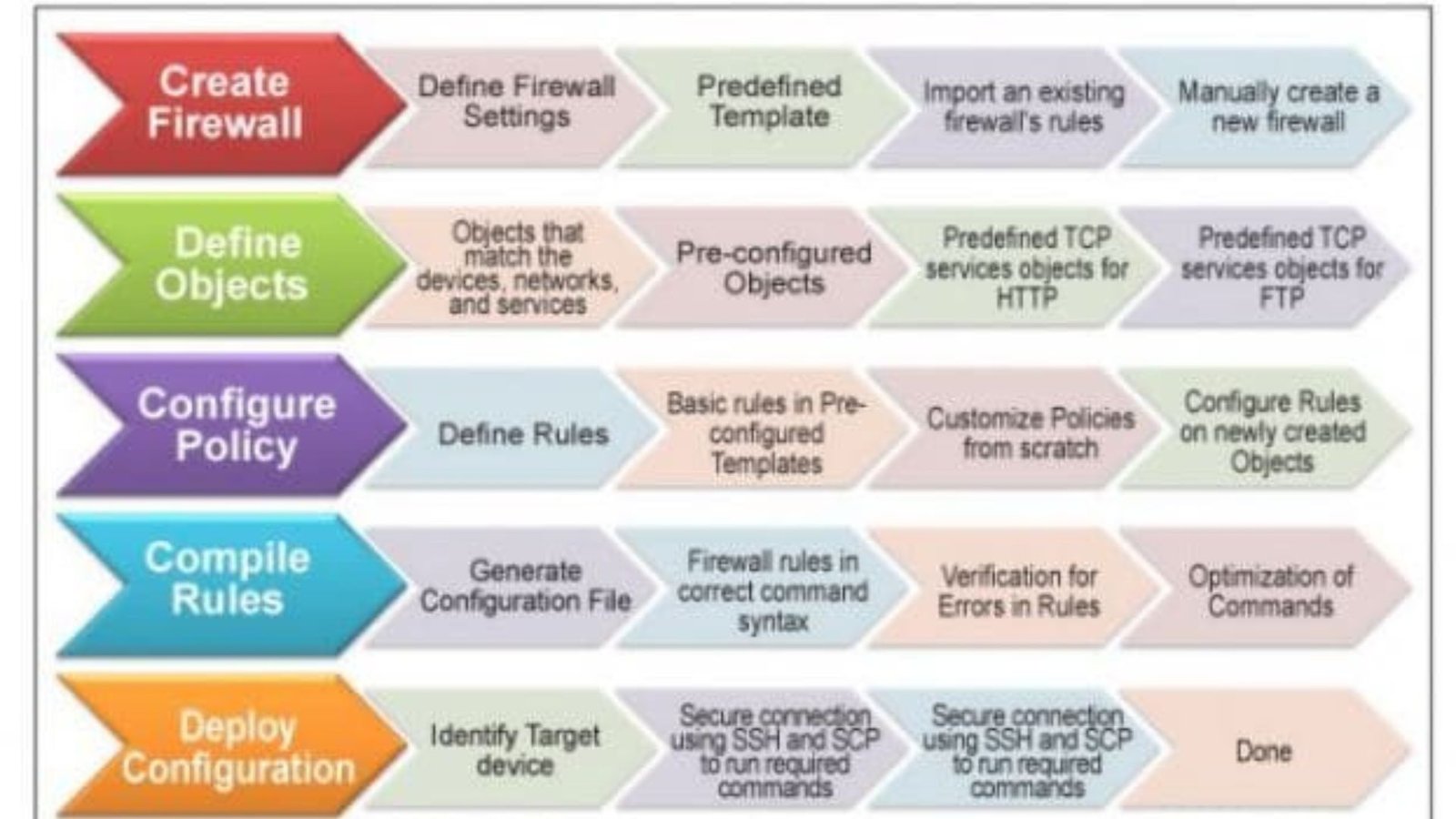
Configuring an initial firewall is a crucial step in securing any network. Firewalls act as the first line of defense, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. A properly configured firewall can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. This article will guide you through the essential steps for setting up your initial firewall configuration to ensure robust network security.

Understanding Firewall Basics
A firewall is a security device that monitors and filters network traffic. It decides whether to allow or block specific traffic based on a defined set of security rules. Firewalls can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both, and they play a vital role in protecting your network from external threats.
When setting up a firewall, it’s essential to understand the basic functions it performs. The primary goal is to create barriers between your internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. By carefully defining what traffic is allowed and what is blocked, you can significantly enhance your network’s security posture.
Planning Your Firewall Configuration
Before you start configuring your firewall, it’s essential to plan your security strategy. Begin by identifying the key assets within your network that need protection. These could include servers, databases, and sensitive data repositories. Knowing what you need to protect will help you define the appropriate security policies and rules.
Next, consider the types of traffic that need to be allowed through the firewall. For example, you might need to allow traffic for web browsing, email services, and specific applications. Conversely, you should block any traffic that is unnecessary or poses a security risk. This planning phase is crucial because it lays the foundation for a secure and efficient firewall configuration.
Implementing Security Policies
Once you’ve planned your firewall configuration, the next step is to implement security policies. These policies dictate how your firewall will handle different types of network traffic.
Start by defining inbound and outbound rules. Inbound rules control the traffic entering your network, while outbound rules manage the traffic leaving your network. It’s generally advisable to adopt a default-deny approach, where all traffic is blocked by default, and only explicitly allowed traffic is permitted. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and ensures that only necessary traffic is allowed.
Additionally, you should create specific rules for different network zones. For example, your internal network, demilitarized zone (DMZ), and external network might each have different security requirements. By segmenting your network and applying tailored security policies to each zone, you can reduce the attack surface and improve overall security.
Testing and Monitoring Your Firewall
After configuring your firewall, it’s vital to test and monitor its performance. Testing helps ensure that your firewall is functioning as intended and that your security policies are effective. Start by running basic connectivity tests to confirm that allowed traffic can pass through the firewall and that blocked traffic is indeed being denied.
You should also perform penetration testing to identify any potential vulnerabilities in your firewall configuration. This process involves simulating attacks on your network to determine whether the firewall can effectively block malicious traffic. Address any identified weaknesses by refining your security policies and adjusting your firewall rules as needed.
Monitoring is equally important in maintaining a secure firewall configuration. Regularly review firewall logs to detect unusual activity or potential security incidents. Logs provide valuable insights into the types of traffic attempting to enter or leave your network, allowing you to identify patterns that could indicate an ongoing attack or a misconfiguration.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
Firewall configuration is not a one-time task; it requires regular updates and maintenance to remain effective. As new threats emerge and your network evolves, you’ll need to adjust your firewall rules and security policies accordingly.
Keep your firewall software up to date with the latest security patches and firmware updates. These updates often address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers, so it’s crucial to apply them as soon as they become available.
In addition to updates, periodically review and refine your firewall rules. Over time, you may find that certain rules are no longer relevant or that new rules are needed to address changing security requirements. Regularly auditing your firewall configuration ensures that it remains aligned with your overall security strategy and that your network remains protected against the latest threats.
Building Your Web Presence and Exploring Online Entertainment
One Cat Web provides web design and development services to help you establish a strong online presence. Just as you focus on creating a purr-fect website, you might also enjoy exploring online entertainment options, and for those interested in virtual gaming platforms in Australia, crazyvegas aus casino offers various platforms. Remember to engage with online activities responsibly while building your digital footprint and enjoying your leisure time.
Conclusion
Configuring an initial firewall is a fundamental step in securing your network against cyber threats. By carefully planning your configuration, implementing robust security policies, testing and monitoring your setup, and maintaining your firewall over time, you can create a strong defense against unauthorized access and other security risks. A well-configured firewall is an essential component of any comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, providing peace of mind and protecting your critical assets from harm.