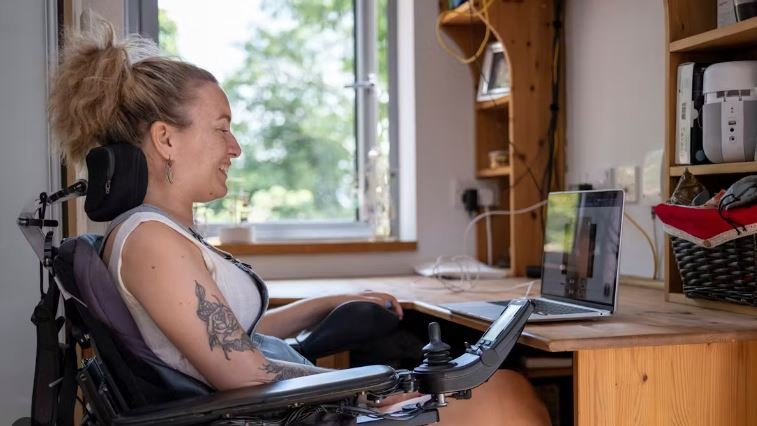
Windows accessibility features help make technology more inclusive by supporting users with disabilities. Microsoft designed these tools to create an adaptable environment that improves the overall computing experience for everyone. With constant updates, Windows continues to enhance its accessibility offerings, ensuring that people of all abilities can fully engage with their devices.
Using Windows for Work and Play
While Windows is well-known for its professional tools and productivity features, it’s also a popular platform for entertainment and relaxation. From gaming to media consumption, Windows supports a wide variety of leisure applications. For users interested in exploring online gaming options, safespin casino bonus australia provides curated offers and secure platforms designed for responsible, casual play.
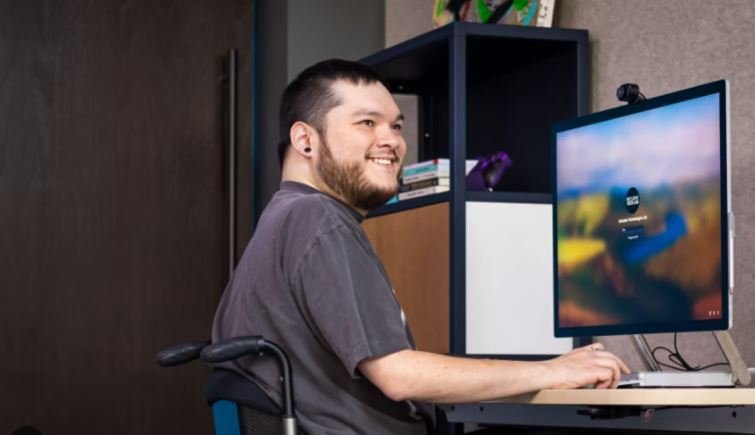

Vision Assistance Features
Windows inclusive technology offer a range of options to support individuals with visual impairments. One of the most widely used tools is the Magnifier, which allows users to zoom in on different parts of the screen. This tool can be activated by pressing the Windows key and the plus (+) sign. Users can customize the zoom level to fit their needs, making it easier to read text and view content.
Narrator is another essential tool for those with visual difficulties. It reads text aloud, guiding users through webpages, documents, and more. Windows also offers High Contrast Mode, which enhances screen colors to make text stand out clearly. Together, these tools help visually impaired individuals navigate technology with ease, ensuring that they don’t miss out on important information.
Hearing Assistance Tools
Windows accessibility features also support individuals with hearing impairments by providing useful sound adjustments. The Mono Audio feature plays all audio through one channel, making it easier for people with hearing loss in one ear to hear content more clearly. Users can activate Mono Audio by going to the Settings menu and navigating to Accessibility > Audio.
Additionally, Windows offers live captions, a feature that generates real-time text for audio content. This tool is helpful for those who need visual support while watching videos or attending virtual meetings. The inclusion of these features makes technology more inclusive for users with different levels of hearing ability, ensuring they can access media without barriers.
Mobility Assistance Features
For individuals with mobility challenges, Windows accessibility features focus on ease of navigation and reducing the need for extensive physical input. The On-Screen Keyboard offers a virtual keyboard that allows users to type by clicking the keys on the screen, which is particularly useful for those who may struggle with a physical keyboard.
Windows also includes Speech Recognition, a tool that enables users to control their device with voice commands. By simply speaking, they can open apps, type documents, and perform tasks. The Sticky Keys feature helps users who have difficulty pressing multiple keys at once by allowing one key to be pressed at a time to execute complex commands. These tools empower individuals with limited mobility to interact with their devices independently.
Cognitive Assistance Tools
Windows accessibility features cater to users with cognitive disabilities by offering tools to simplify the interface. One key feature is Focus Assist, which reduces distractions by blocking non-essential notifications while users work. This tool is particularly helpful for individuals with attention difficulties, as it allows them to focus on tasks without interruptions.
Another helpful tool is the Read Aloud feature in Microsoft Edge, which reads webpages aloud to support users with reading difficulties. Additionally, Windows offers Color Filters to assist individuals with color blindness, allowing them to adjust the screen display for better visual clarity. These tools enhance the overall user experience for people with cognitive challenges, helping them navigate technology in a way that meets their needs.
Conclusion
Windows accessibility features play a vital role in making technology more inclusive for users of all abilities. Whether through vision, hearing, mobility, or cognitive assistance tools, Microsoft has built an adaptable system that empowers individuals to engage with their devices fully. By leveraging these features, Windows continues to make technology accessible for everyone, promoting inclusion in the digital world.