Integrating Windows with Microsoft Azure. As businesses and individuals increasingly migrate to the cloud, the integration between Windows and Microsoft Azure has become more critical than ever. This powerful combination offers seamless connectivity, robust security, and the flexibility to scale resources on demand. Whether you’re running a small business or managing a large enterprise, understanding how to integrate Windows with Azure can unlock new levels of productivity and efficiency.
1. Understanding Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that provides a wide range of services, including virtual machines, databases, storage, and networking. It allows businesses to deploy, manage, and scale applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers.
Integrating Azure with your Windows environment means leveraging these services to enhance your IT infrastructure, whether for hosting applications, storing data, or managing workloads.
2. Setting Up Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a cloud-based identity and access management service. It is crucial for managing user identities and controlling access to resources. Integrating Windows with Azure AD allows for seamless user authentication across both on-premises and cloud-based resources.
Steps to Integrate:
- Join Windows Devices to Azure AD: You can join Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices directly to Azure AD, which simplifies sign-in and access to Azure resources.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Enable SSO so users can access both on-premises and cloud apps with a single login.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance security by requiring additional verification for users accessing sensitive data.
3. Deploying Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD)
Windows Virtual Desktop is a comprehensive desktop and app virtualization service running on Azure. It allows users to access a full Windows experience from any device, anywhere.
Key Features:
- Scalability: Easily scale the number of virtual desktops based on user demand.
- Cost-Efficiency: Only pay for what you use, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.
- Security: Benefit from Azure’s built-in security features, including encryption and advanced threat protection.
Steps to Deploy:
- Set Up Your Azure Environment: Ensure your Azure subscription is configured and ready.
- Create a Host Pool: Set up a host pool in the Azure portal to manage your virtual machines.
- Assign Users: Assign users to the Windows Virtual Desktop service, allowing them to access their virtual desktops.
4. Using Azure Backup for Windows
Azure Backup is a scalable solution that protects your data with automated backups stored in the cloud. Integrating Azure Backup with your Windows environment ensures that your critical data is protected and easily recoverable.
Steps to Implement:
- Install the Azure Backup Agent: Download and install the Azure Backup Agent on your Windows server or machine.
- Configure Backup Policies: Set up policies that define how often backups are taken and how long they are retained.
- Monitor and Manage Backups: Use the Azure portal to monitor backup status and manage recovery points.
5. Azure Site Recovery (ASR) for Windows
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a disaster recovery solution that replicates your Windows environment to Azure, ensuring business continuity during outages.
Steps to Implement:
- Set Up ASR: In the Azure portal, configure ASR to replicate your on-premises Windows servers to Azure.
- Test Failover: Perform a test failover to ensure that your recovery plan works as expected.
- Automate Failover: Automate the failover process to reduce downtime in case of a disaster.
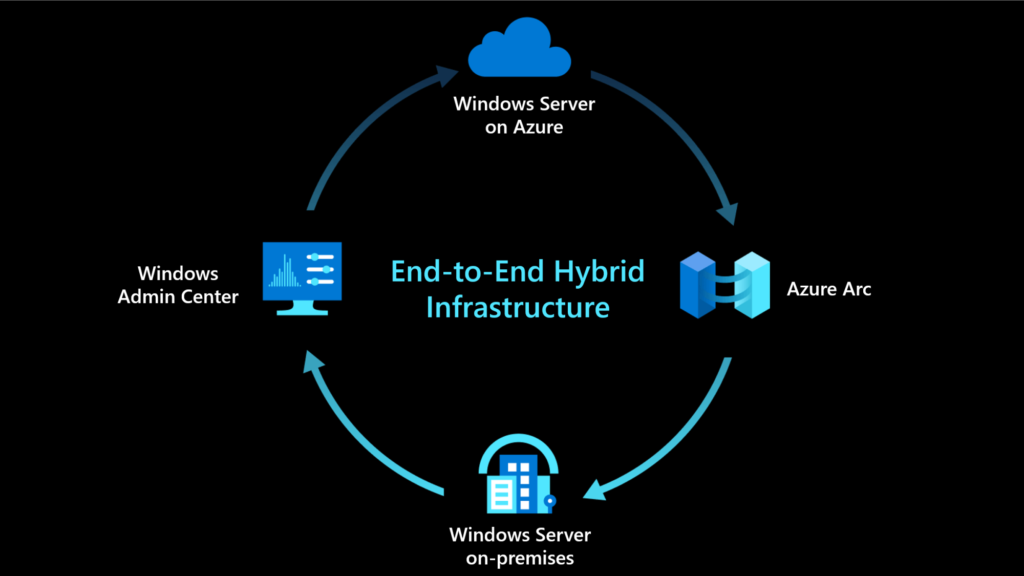
6. Hybrid Cloud Solutions with Azure Arc
Azure Arc allows you to extend Azure management and services to any infrastructure, including on-premises, multi-cloud, and edge environments. This integration enables you to manage Windows servers and services across different environments from a single control plane.
Key Features:
- Centralized Management: Manage all your Windows servers, whether on-premises or in the cloud, from the Azure portal.
- Compliance and Security: Apply consistent security policies across your hybrid environment.
- Application Management: Deploy and manage applications using Kubernetes across various environments.
Conclusion
Integrating Windows with Microsoft Azure offers a powerful combination of cloud flexibility, robust security, and enhanced productivity. By leveraging Azure’s services, businesses can optimize their IT infrastructure, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. Whether you’re looking to enhance identity management with Azure AD, deploy virtual desktops, or ensure business continuity with Azure Site Recovery, the integration between Windows and Azure provides the tools needed to meet your business goals.