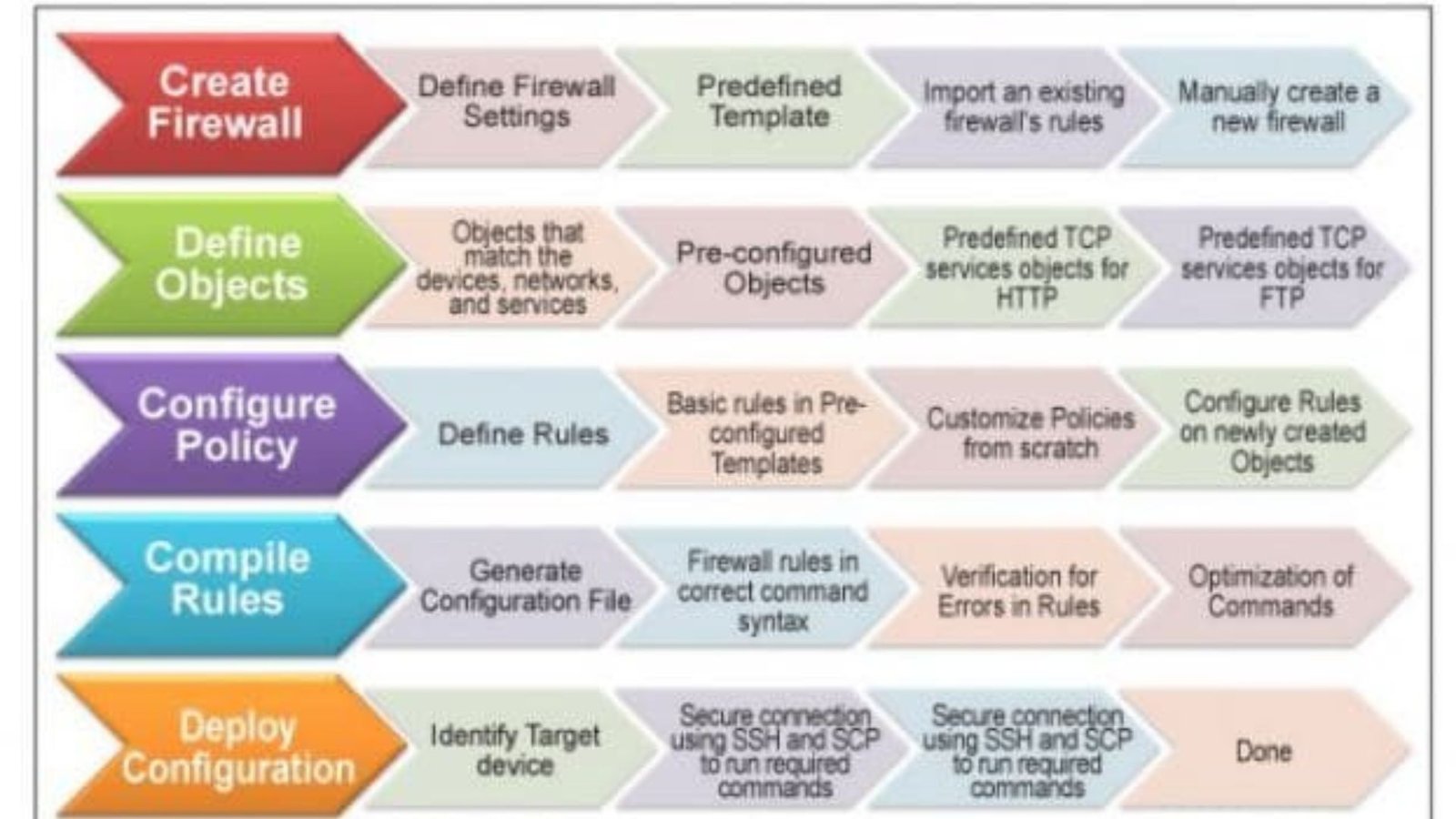
Monitoring and auditing firewall activity is essential for maintaining network security, detecting potential threats, and ensuring compliance with security policies. Proper monitoring and auditing help identify anomalies, respond to incidents, and optimize firewall configurations. Here’s a guide to effectively monitor and audit firewall activity.
Understand Your Firewall’s Logging Capabilities
Log Types:
Firewalls generate various types of logs, including traffic logs, event logs, and security logs. Understanding what each log contains is crucial for effective monitoring. Traffic logs track the data passing through the firewall, while event logs capture firewall events such as configuration changes. Security logs provide insights into blocked or allowed connections based on security policies.
Log Settings:
Configure your firewall to capture relevant logs by adjusting the logging settings. Ensure that logs are detailed enough to provide valuable information without overwhelming you with unnecessary data. Set up logging for critical events such as denied connections, policy changes, and system alerts.
Implement a Centralized Logging System
Log Aggregation:
Centralizing logs from multiple firewalls into a single system simplifies monitoring and analysis. Use log management tools or Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to aggregate and correlate data from different sources. Centralized logging enables you to get a comprehensive view of network activity and simplifies the process of identifying and responding to threats.
Log Retention:
Establish a log retention policy to ensure that logs are kept for a sufficient period. This is essential for historical analysis, compliance requirements, and forensic investigations. Determine the appropriate retention period based on regulatory requirements and organizational needs.
Set Up Real-Time Monitoring
Alerts and Notifications:
Configure alerts and notifications to be informed of critical events as they occur. Set thresholds for specific types of activity that may indicate potential security incidents or system issues. For example, configure alerts for multiple failed login attempts, unusual traffic spikes, or configuration changes.
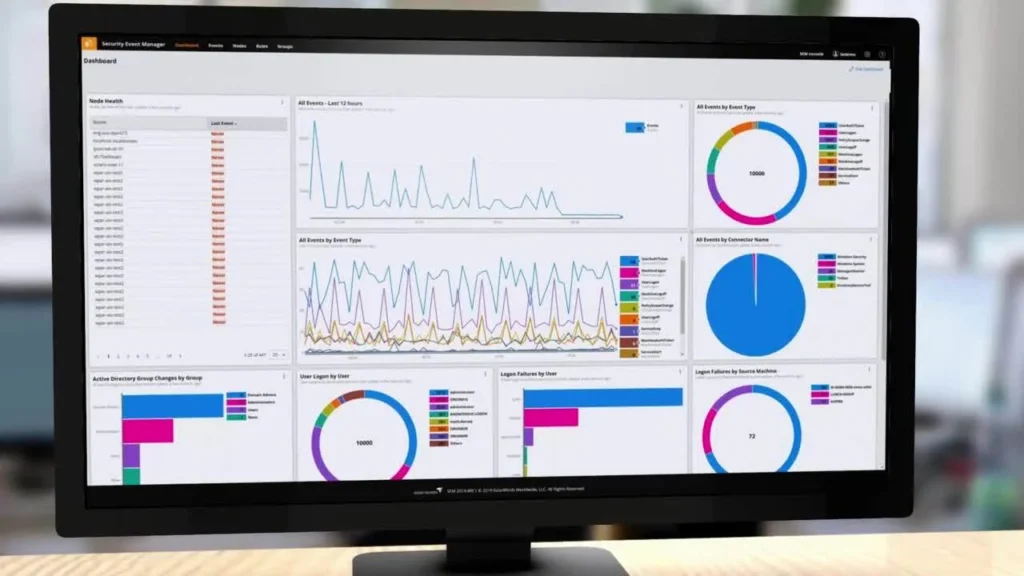
Dashboard and Visualization:
Utilize dashboards and visualization tools to monitor firewall activity in real-time. Dashboards provide an overview of current traffic patterns, security events, and system health. Visual representations of data make it easier to spot anomalies and trends.
Regularly Review and Analyze Logs
Log Analysis:
Regularly review firewall logs to identify patterns and potential security incidents. Analyze traffic patterns, connection attempts, and blocked requests to detect unusual behavior or policy violations. Use automated tools and scripts to assist in analyzing large volumes of log data.
Anomaly Detection:
Look for signs of unusual activity that could indicate security threats, such as unexpected traffic sources, abnormal connection attempts, or repeated access attempts to restricted areas. Implement anomaly detection tools to help identify deviations from normal behavior.
Conduct Periodic Audits
Audit Scope:
Perform regular audits of firewall configurations and logs to ensure compliance with security policies and standards. Audits should include a review of firewall rules, access controls, and log data to verify that they align with organizational security requirements.
Audit Checklist:
Develop a checklist for firewall audits, covering areas such as rule configurations, logging settings, alerting mechanisms, and compliance with internal and external regulations. Regular audits help identify misconfigurations, outdated rules, and potential security gaps.
Ensure Compliance with Security Policies
Policy Review:
Regularly review and update firewall policies to ensure they reflect current security needs and compliance requirements. Ensure that firewall rules are aligned with organizational security policies and best practices.
Documentation:
Maintain detailed documentation of firewall configurations, rule changes, and log management practices. Proper documentation supports effective auditing, troubleshooting, and compliance verification.
Respond to Security Incidents
Incident Response Plan:
Develop and implement an incident response plan for addressing security incidents detected through firewall logs and monitoring. Define procedures for investigating, containing, and mitigating security breaches. Ensure that your response plan includes steps for analyzing firewall logs and taking corrective actions.
Forensic Analysis:
In the event of a security incident, perform forensic analysis of firewall logs to understand the nature of the attack, its impact, and how it bypassed existing defenses. Use this information to improve firewall configurations and prevent future incidents.
Conclusion
Monitoring and auditing firewall activity are critical for maintaining network security and ensuring that your firewall operates effectively. By understanding your firewall’s logging capabilities, implementing centralized logging, setting up real-time monitoring, and conducting regular audits, you can enhance your ability to detect and respond to security threats. Regular reviews, compliance checks, and incident responses further strengthen your network’s security posture and resilience.