Introduction to Firewalls
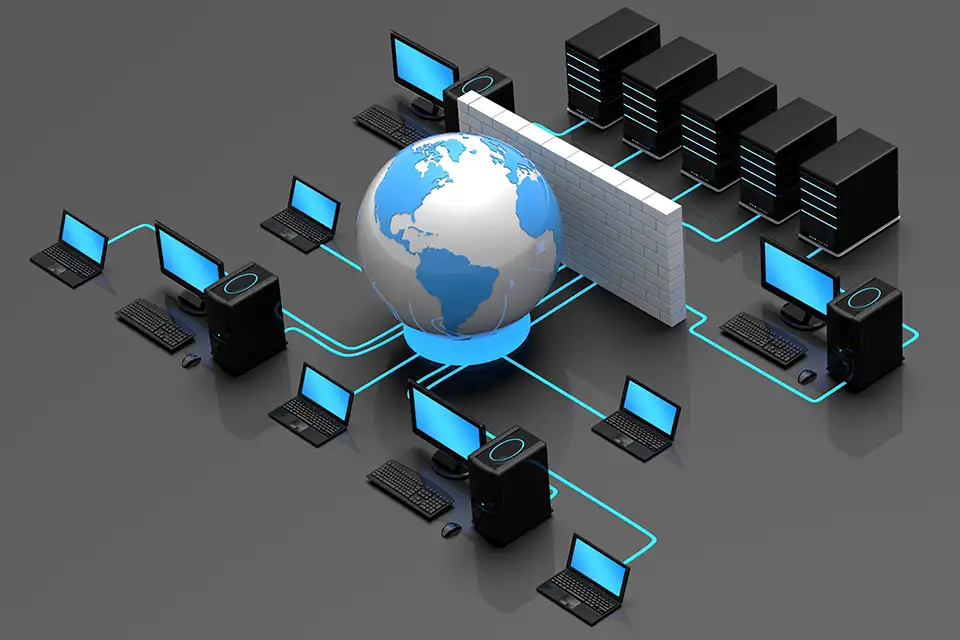
In today’s digital landscape, protecting network security is crucial. Firewalls are fundamental tools in this protection. They act as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks. Their primary purpose is to block unauthorized access while permitting legitimate communication.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic. It can be hardware, software, or a combination of both. By enforcing a set of security rules, firewalls prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Types of Firewalls
There are several types of firewalls, each with unique features and uses:
- Packet-Filtering Firewalls: These are the simplest type. They examine packets of data and allow or block them based on predefined rules.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: These track active connections and make decisions based on the state of the connection.
- Proxy Firewalls: They act as intermediaries between users and the internet, hiding the user’s IP address and blocking unwanted content.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): These combine traditional firewall capabilities with advanced features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS), application awareness, and threat intelligence.

How Firewalls Protect Your Network
Firewalls protect networks by filtering traffic and enforcing security policies. They can block malicious software, prevent unauthorized access, and control the flow of data. This makes them essential in safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining network integrity.
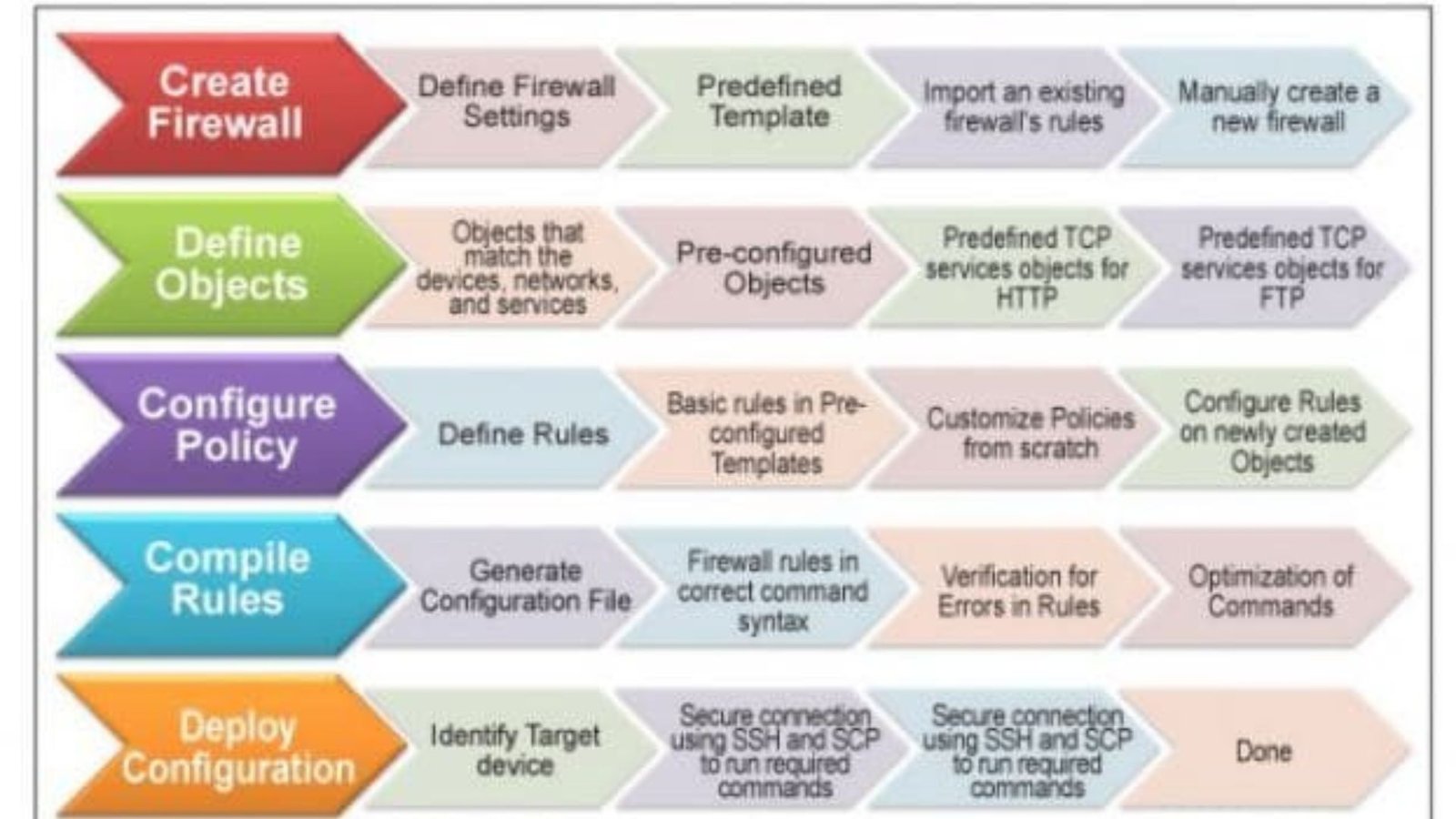
Configuring a Firewall
Proper configuration is vital for a firewall to function effectively. It involves setting up rules that define what traffic is allowed or blocked. Administrators must regularly update these rules to address new threats and ensure that the firewall remains effective against evolving cyber-attacks.
Firewalls and Network Layers
Firewalls operate at different layers of the network. For instance:
- Network Layer: Firewalls at this layer focus on IP addresses and ports. They filter traffic based on source and destination addresses.
- Application Layer: Firewalls at this layer scrutinize the data within packets. They ensure that applications are functioning correctly and protect against application-level attacks.
Benefits of Using Firewalls
Using firewalls offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Firewalls provide a first line of defense against external threats. They help prevent unauthorized access and mitigate risks.
- Controlled Access: They allow administrators to set specific rules about who can access certain network resources.
- Traffic Monitoring: Firewalls can log network activity, helping in monitoring and troubleshooting security incidents.
Challenges and Limitations
While firewalls are essential, they are not foolproof. They cannot protect against all types of cyber threats. For instance, they might not detect insider threats or zero-day vulnerabilities. Regular updates and additional security measures are necessary to address these limitations.
Best Practices for Firewall Management
To maximize the effectiveness of firewalls, follow these best practices:
- Regular Updates: Ensure that the firewall’s firmware and rules are up-to-date to defend against new threats.
- Monitor Logs: Regularly review firewall logs for suspicious activity or potential breaches.
- Implement Layered Security: Use firewalls in conjunction with other security measures like antivirus software and intrusion detection systems.
Conclusion
Firewalls are a crucial component of network security. They help protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats by monitoring and controlling traffic. Understanding how they work and following best practices ensures they provide effective protection. Regular updates and proper configuration are essential for maintaining a secure network environment.