Introduction to Firewalls
The Role of Firewalls in Modern Cybersecurity. Firewalls are critical components in modern cybersecurity. They act as barriers between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks. Their primary role is to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data from cyber threats.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. It can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both. By analyzing network traffic, firewalls ensure that only authorized users and applications can access the network.
Types of Firewalls
Firewalls come in various types, each serving different purposes:
- Packet-Filtering Firewalls: These are the most basic type. They examine packets of data and decide whether to allow or block them based on defined rules such as IP addresses and port numbers.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: These firewalls keep track of active connections and make decisions based on the state of these connections, providing more dynamic and secure filtering.
- Proxy Firewalls: Proxy firewalls act as intermediaries between users and the internet. They mask users’ IP addresses and filter content to prevent access to harmful sites.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): NGFWs integrate traditional firewall functions with advanced features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS), application awareness, and threat intelligence, offering enhanced protection.
How Firewalls Enhance Cybersecurity
Firewalls play a crucial role in cybersecurity by providing several key benefits:
- Blocking Unauthorized Access: They prevent unauthorized users and applications from accessing the network, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks.
- Monitoring Traffic: Firewalls monitor network traffic to identify and block suspicious activity, which helps in detecting and preventing potential threats.
- Enforcing Security Policies: By applying security rules and policies, firewalls help enforce organizational security standards and ensure compliance with regulations.
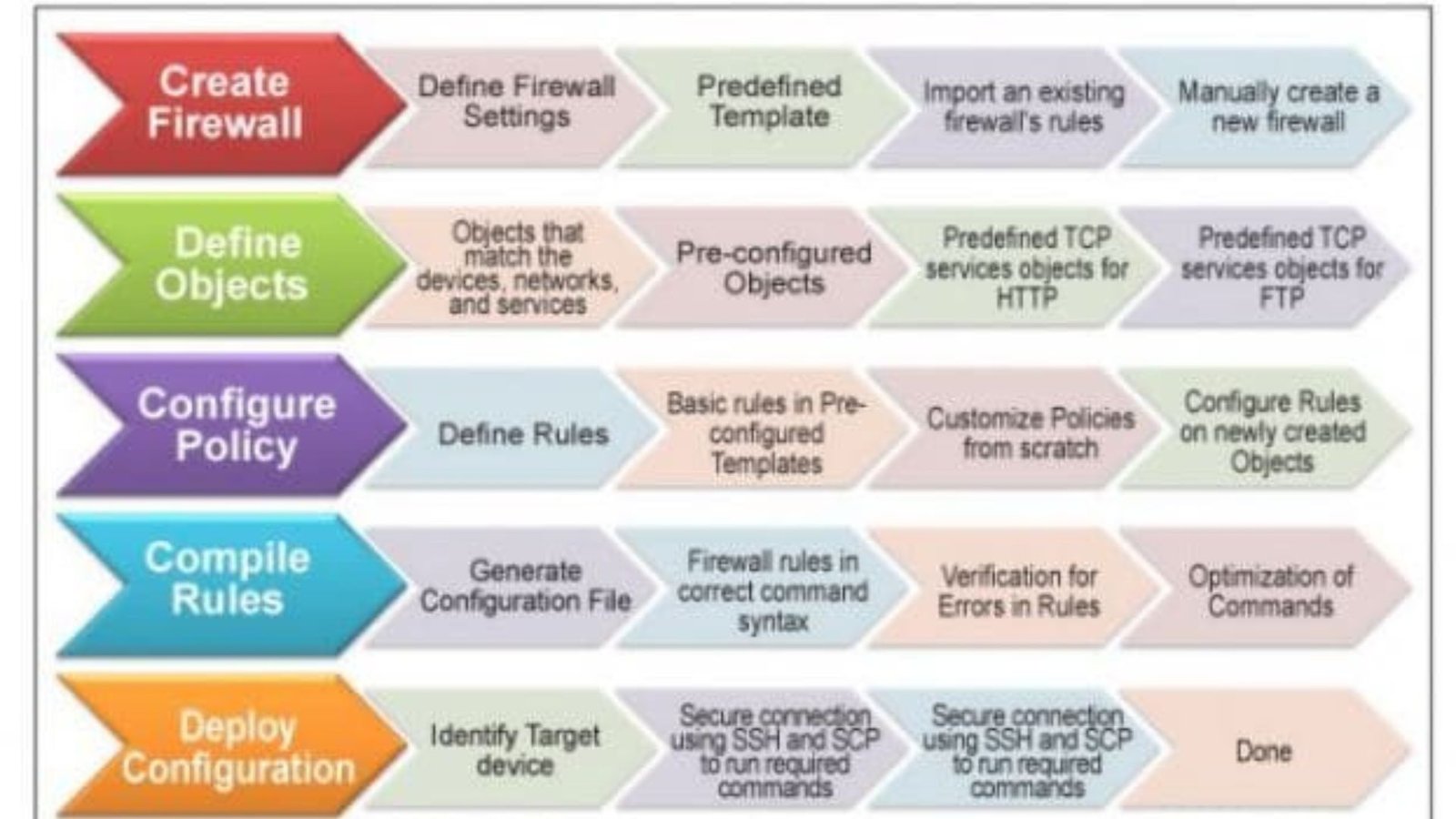
Configuring and Managing Firewalls
Effective firewall management involves proper configuration and regular updates:
- Setting Up Rules: Administrators must configure rules to define what traffic is allowed or blocked. These rules should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs and updated regularly.
- Updating Firmware: Keeping the firewall’s firmware up-to-date is essential for protecting against new vulnerabilities and threats.
- Monitoring Logs: Regularly reviewing firewall logs helps in identifying potential security incidents and understanding network activity.
Firewalls in Multi-Layered Security Strategies
Firewalls are just one part of a comprehensive security strategy. Combining them with other security measures enhances overall protection:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS can detect and alert on suspicious activities that firewalls might not catch.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus programs help protect against malware that could bypass firewall defenses.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it is intercepted, it remains protected.

Challenges and Limitations
While firewalls are vital, they have limitations:
- Cannot Prevent All Threats: Firewalls alone cannot protect against all types of cyber threats, such as insider attacks or zero-day exploits.
- Complex Configurations: Incorrect configuration can lead to security gaps, making it crucial to have skilled personnel manage and maintain firewalls.
- Performance Impact: High levels of traffic or complex rules can affect network performance, making it important to balance security with efficiency.
Best Practices for Using Firewalls
To maximize the effectiveness of firewalls, consider the following best practices:
- Regular Updates: Keep firewalls and their rules updated to defend against new threats and vulnerabilities.
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Continuously monitor network traffic and firewall logs for unusual activities or potential breaches.
- Layered Defense: Use firewalls alongside other security measures for a robust defense against various cyber threats.
Conclusion
Firewalls are essential tools in modern cybersecurity, providing crucial protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats. By understanding their role, types, and best practices for management, organizations can enhance their network security and safeguard sensitive data effectively. Regular updates and proper configuration are key to maintaining a secure network environment.